-
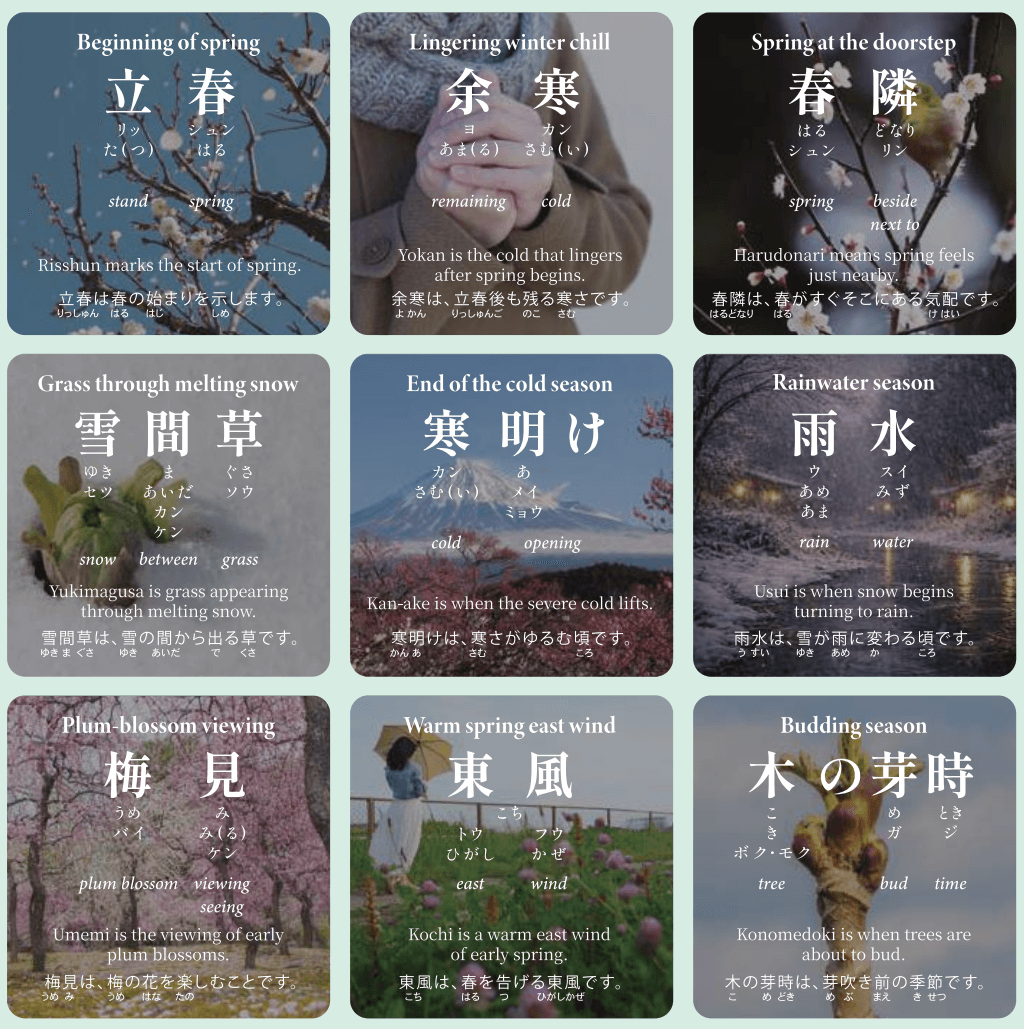
Seasonal Voice-Word Art: “January slips away, February runs away, March goes away” — the early months of the year pass in the blink of an eye.
季節の言技:「一月往ぬる二月逃げる三月去る」― 年のはじめ三か月は、あっという間に過ぎていく。- Hiragana Times
- Jan 28, 2026
[NIHONGO DO – Voice-word Art – February 2026 Issue]
Seasonal Voice-Word Art: “January slips away, February runs away, March goes away” — the early months of the year pass in the blink of an eye.
季節の言技:「一月往ぬる二月逃げる三月去る」― 年のはじめ三か月は、あっという間に過ぎていく。
This “Voice-Word Art” section introduces seasonal words related to the time of year. Enjoy the timeless beauty of these artistic expressions.
この「言技」セクションでは、季節にちなんだ季語を紹介しています。時代を超えて響く言葉のアート(言技)をお楽しみください。
一月往ぬる二月逃げる三月去る
“January slips away, February runs away, March goes away.”
This proverb expresses the sense that the first three months of the year pass with surprising speed. January begins with celebrations, February is short and hurried, and March carries us toward spring. It reminds us that time flows quickly—urging us to savor each moment with care.
年の始まりの三か月は、驚くほど早く過ぎてしまう――そんな季節感を表す言葉です。行事の多い一月、短く慌ただしい二月、そして春へ向かう三月。めまぐるしく過ぎゆく時のなかで、一日一日を大切に生きたいという思いをそっと呼び起こします。
■ Meaning / 意味
Ichigatsu inuru: January “goes away”; the month slips quietly past.
一月 往ぬる:一月はすっと過ぎていく。
Nigatsu nigeru: February “runs away”; short and fast-moving.
二月 逃げる:二月は逃げるように過ぎる。
Sangatsu saru: March “goes away”; carried off toward spring.
三月 去る:三月は春に向かって去っていく。
■ Usage / 使う場面
A: I can’t believe it’s already mid-February.
A: もう二月の半ばなんて信じられないよ。
B: Same here. I haven’t done half the things I planned.
B: 本当。やりたいことの半分もできてない。
A: Well, you know the saying, “January slips away, February runs away, March goes away.”
A: 「一月往ぬる二月逃げる三月去る」って言うじゃない。
B: True… if I don’t move now, spring will be here before I know it.
B: そうだね…。このままだと、気づいたら春になってそう。
This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
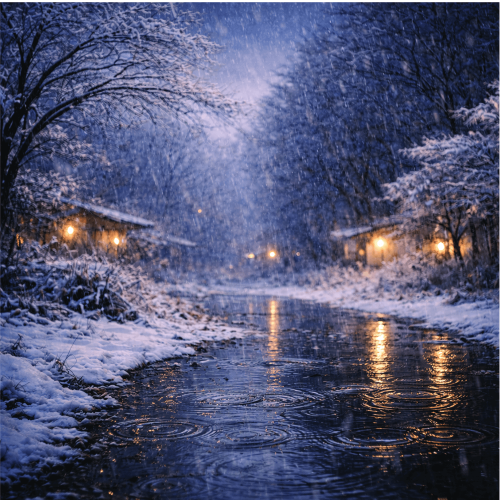
Seasonal Word Leaves: Japan’s February, “Kisaragi” — lingering winter chill, early spring signs, and days that seem to slip away.
季節の言の葉:日本の2月「如月(きさらぎ)」— 残る寒さと芽吹きの気配、そして足早に過ぎていく日々。- Hiragana Times
- Jan 28, 2026
[NIHONGO DO – Word Leaves – February 2026 Issue]
Seasonal Word Leaves: Japan’s February, “Kisaragi” — lingering winter chill, early spring signs, and days that seem to slip away.
季節の言の葉:日本の2月「如月(きさらぎ)」— 残る寒さと芽吹きの気配、そして足早に過ぎていく日々。
There is a well-known theory that “Kisaragi” means the month when people layered their garments to endure the lingering cold. Even as the chill remains, plum buds begin to open, the east wind softens the ice, and the first hints of spring quietly slip in. Time seems to move quickly, and as the saying goes, “February runs away,” the days pass in a moment. In this blend of severity and gentleness, a uniquely crisp beauty emerges in this season.
如月には、「寒さの中で衣(きぬ)をさらに重ねる月(衣更着)」とする説が広く知られています。冷え込みが残るなか、梅の蕾がほころび、東風が氷をゆるめ、春の気配が静かに差し込みます。時間はどこか急ぎ足で、「二月逃げる」という言い伝えのとおり、日々は瞬く間に過ぎていきます。厳しさとやわらぎが交わる、この時季ならではの凛とした美しさが宿ります。

This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
National Foundation Day — A Day to Reflect on Japan’s Beginnings
建国記念の日――日本の「はじまり」を考える日- Hiragana Times
- Jan 28, 2026
[Japan savvy – February 2026 Issue]
National Foundation Day — A Day to Reflect on Japan’s Beginnings
建国記念の日――日本の「はじまり」を考える日
February 11th, which is ‘National Foundation Day’, is the day when it is said that the first Emperor, Emperor Jimmu, ascended the throne.
「建国記念の日」である2月11日は、初代天皇・神武天皇が即位したと伝えられる日です。
That year is considered to be 660 BC, and His Majesty the current Emperor corresponds to the 126th generation counting from there.
その年は紀元前660年とされ、現在の天皇陛下は、そこから数えて126代目にあたります。
It was in the Meiji era, when relationships with Western powers began to deepen, that this day was first established.
この日が最初に定められたのは、「西洋列強」との関係が深まりはじめた明治時代でした。
Japan named this day ‘Kigensetsu’ in order to show its own origin to the international community.
日本は国際社会に向けて、自らの起源を示すため、この日を「紀元節」と名づけました。
After World War II, Kigensetsu was abolished once under the occupation policy, but after that, receiving the voices of the people, it revived changing its name to ‘National Foundation day.
第二次世界大戦後、占領政策のもとで紀元節はいったん廃止されますが、その後、国民の声を受けて「建国記念の日」と名を変えて復活します。
In Japanese mythology, there is a story called ‘Kuniyuzuri’ (Transfer of the Land), which is said to have ceded the country to the lineage of Emperor Jimmu.
日本の神話には、神武天皇の系譜に国を譲ったとされる「国譲り」という物語があります。
In it, it is told that a ‘country’ existed in this Japan even before ‘Kigensetsu’.
そこには、「紀元節」以前にも、この日本に「国」が存在していたことが語られています。
National Foundation Day is a day to turn one’s thoughts to Japan’s endlessly long history.
建国記念の日は、日本の果てしなく長い歴史に想いを馳せる日です。
Become a Kenkoku Savvy 建国通になる
WARM UP | Kenkoku JapaNEEDS
Useful Words 役立つ言葉
- 建国記念の日(けんこくきねんのひ) – National Foundation Day
- 即位(そくい) – enthronement; accession to the throne
- 神武天皇(じんむてんのう) – Emperor Jimmu
- 紀元前(きげんぜん) – BCE (Before the Common Era)
- 紀元節(きげんせつ) – National Foundation Day
- 起源(きげん) – origin
- 国際社会(こくさいしゃかい) – international community
- 神話(しんわ) – mythology
- 国譲り(くにゆずり) – transfer of the land (myth)
- 系譜(けいふ) – lineage
- 歴史(れきし) – history
- 想いを馳せる(おもいをはせる) – to reflect on; to think back
Ice Breaker Questions 会話のきっかけ
1.Does your country have a day that commemorates its founding?
あなたの国には、「建国」を記念する日がありますか?
2.What kind of event is that day based on?
その日は、どんな出来事をもとに定められていますか?
3.Do you think a nation’s beginning can be clearly defined?
「国のはじまり」は、はっきり決められるものだと思いますか?
4.Do you see mythology as history, or as a story?
神話は、歴史だと思いますか?それとも物語だと思いますか?
5.What kind of day makes you feel a sense of “beginning”?
あなたにとって、「はじまり」を感じる日はどんな日ですか?
WORK UP | Kenkoku Discussion
DISCUSSION ディスカッション
Michael: America’s Independence Day is July 4th, marking 1776, when the Declaration of Independence was issued.
マイケル:アメリカの建国記念日は、1776年に独立宣言が出された7月4日です。
Mayumi: That was the day George Washington and others declared independence from Britain, right?
まゆみ:ジョージ・ワシントンたちがイギリスからの独立を宣言した日ですね。
Emily: The UK doesn’t actually have a “National Foundation Day.”
That’s because our monarchy and political system evolved gradually over time.エミリー:イギリスには、実は「建国記念日」はありません。王朝や国の形が、少しずつ変わってきたからです。
Ming:In China, we celebrate National Day on October 1st, marking 1949, when Mao Zedong proclaimed the founding of the People’s Republic of China.
ミン:中国では、1949年10月1日に毛沢東が中華人民共和国の成立を宣言した日を、「国慶節」として祝います。
Pierre: In France, we celebrate July 14th to commemorate the French Revolution of 1789. Our nation begins not with a dynasty, but with the revolution itself.
ピエール:フランスでは、1789年のフランス革命を記念する7月14日を祝います。王朝のはじまりではなく、「革命」そのものが国の出発点なんです。
Mayumi: Looking at it this way, many countries define their beginnings through clear historical events. In Japan, however, the founding of the nation is told alongside mythology.
まゆみ:こうして見ると、多くの国は、はっきりした「歴史的な出来事」を建国の始まりにしているんですね。日本の場合、建国は神話と重ねて語られます。
Emily: That’s the story in which the land of Izumo was said to have been handed over to the lineage of Emperor Jimmu, a descendant of the sun deity, right?
エミリー:出雲の国が、太陽の神の子孫である神武天皇の系譜に、国を譲ったという物語ですね。
Ming: The birth of the nation itself sounds almost like a Studio Ghibli film.
ミン:国の誕生そのものが、まるでジブリアニメみたいですね。
Pierre: Anime, or should I say, animism. That’s what you’d expect from a country rooted in nature worship.
ピエール:アニメならぬ、アニミズム。自然崇拝の国ならではですね。
WORK UP | Osechi Discussion
DISCUSSION ディスカッション
In Japan, people are given a posthumous name (okurina) based on how they lived and what they achieved after their death.
日本では、死後その人の生き方や功績などをもとに、諡(おくりな)が与えられます。
The name Emperor Jimmu is also a posthumous title; his name during his lifetime was Iwarebiko (Kamuyamato Iwarebiko).
神武天皇という名も諡であり、生前の名はイワレビコ(神日本磐余彦〈かむやまと・いわれびこ〉)でした。
It is said that before the establishment marked by Kigensetsu, there existed what is often referred to as the Izumo dynasty.
紀元節以前には、「出雲王朝」が存在したと伝えられています。
The Japanese archipelago is crossed by mountain ranges that run like a backbone through the land; the Sea of Japan side is called San’in, while the Pacific side is known as San’yō.
日本列島には山脈が背骨のように連なり、日本海側は山陰、太平洋側は山陽と呼ばれています。
In Japan, Hyuga City in Kyushu is written as “where the sun turns,” Hitachi City in eastern Japan as “where the sun stands,” and Izumo City in the San’in region as “where clouds appear.”
日本には、日が向かうと書く「日向市」が九州に、日が立つと書く「日立市」が東日本に、そして雲が出る「出雲市」が山陰にあります。
“Izumo,” now located in Shimane Prefecture, is thought in ancient times to have extended its influence from the Sea of Japan coast, across the mountains, and into the Nara Basin, a key geographical crossroads.
現在、島根県に位置する「出雲」は、古代においては、日本海側から山々を越えた、地形の切れ目である奈良盆地にまで、その影響を及ぼしていたと考えられています。
Iwarebiko (Emperor Jimmu) is said to have been born in the area around Hyuga in Kyushu.
イワレビコ(神武天皇)は、九州の日向のあたりで生まれたと伝えられています。
In the story of his eastern expedition toward Nara, there appears a figure named Nigihayahi, who is described as having ruled the Kinai region before Jimmu.
イワレビコが奈良へと向かう東征の物語には、ニギハヤヒ(饒速日)と呼ばれる、神武天皇以前に畿内を統治していたとされる存在が語られています。
Some scholars view Nigihayahi as a ruler who preceded Emperor Jimmu—sometimes described as a kind of “zero-generation emperor.”
このニギハヤヒ(饒速日)を、神武天皇以前の支配者、いわば「ゼロ代天皇」のような存在として捉える研究者もいます。
This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
[JAPAN MAZE | 迷宮ニホン – February 2026 Issue]
You may understand the words, but still get lost in communication. This corner takes you on a fun journey through the maze of Japanese language and culture with four-panel manga. Unlocking the punchline is the key – it reveals the essence of Japanese expression and leads you to the exit, with a smile and a fresh insight.
言葉の意味はわかるのに、なぜか通じない――。日本語と日本文化の迷宮を、4コマ漫画で楽しく探検するコーナーです。 “オチ”を読み解けば、日本語の本質が見えてくる。迷宮の出口には、気づきと笑いが待っています。
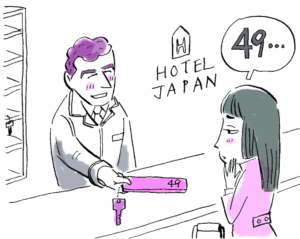
チェックイン | Check in
Scene 1

スタッフ:ごゆっくりどうぞ。
Staff : Take your time.日本人客:でも、番号がシキュウ。
Japanese guest : But, the number reads shikyuu (urgent).Scene 2

スタッフ:お部屋の番号が気になりますか。
Staff: Are you concerned about room numbers?日本人客:縁起の悪い数字ですからね。
Japanese guest : I am, because it’s an unlucky number.Scene 3

スタッフ:では、53号室が空いてますが …… 。
Staff : Well then, room 53 is available.日本人客:今度はゴミ部屋?
Japanese guest : This time it’s the garbage room is it?Scene 4

スタッフ:すみません。39号室はいかがですか。
Staff : I’m sorry. How about room 39?日本人客:いいですね。サンキュウ。
Japanese guest : Good. Thank you.
Maze Navigation / 迷宮ナビ
Let’s break down each scene | それぞれのシーンを理解しよう。Scene 1
At hotel check-in, the staff assigns Room 49. In Japanese, 4 is read “shi” and 9 is read “ku,” and together they form shikyuu, meaning “urgent.”
ホテルのチェックイン。スタッフは49号室を案内します。日本では、4は「し」、9は「きゅう」と読み、合わせると「至急」という意味になります。そのため、「しきゅう」と言われた案内と、部屋番号の意味が矛盾します。
■ 案内する [to guide / to assign]
■ 至急 [urgent]
■ 意味 [meaning]
■ 矛盾する [to contradict]Scene 2
The receptionist thinks the guest is simply worried about the room number. In Japan, both 4 (shi) and 9 (ku/kyuu) are seen as unlucky: shi sounds like “death,” and ku sounds like “suffering.” This superstition makes the guest uneasy.
スタッフは、お客が番号を気にしているのだと思っています。日本では、4(し)は「死」、9(く/きゅう)は「苦」と連想させる不吉な数字とされています。そのため、客はどうしても気になってしまいます。
■ 番号 [number]
■ 気にする [to be concerned about]
■ 不吉 [unlucky / ominous]
■ 死 [death]
■ 苦 [suffering / hardship]Scene 3
Now the guest is being shown to Room 53. But 5 can be read go and 3 can be read mi, which together form gomi (“garbage”). So the guest can’t help thinking, “A garbage room?”
今度は53号室を案内します。しかし、5は「ご」、3は「み」とも読み、続けると「ゴミ」になります。そのため客は「ゴミ部屋?」と連想してしまいます。
■ 続ける [to put together / to combine]
■ ごみ [garbage / trash]
■ 連想する [to associate with / to be reminded of]Scene 4
Finally, they suggest Room 39. The number 39 can be read san-kyuu, which sounds very close to “thank you” in English. This kind of wordplay is something many Japanese people enjoy.
最後は39号室を提案しました。39は「サンキュー」と読めるため、英語の “thank you” によく似た音になります。こうした語呂合わせは、日本人にとても親しまれています。
■ 提案する [to suggest]
■ 語呂合わせ [wordplay / pun]
■ 親しまれている [be liked / be familiar to]
Maze Exit / 迷宮出口
What did the punchline reveal? / 今回のオチでわかったことCultural Insight / 新しい発想・文化知識
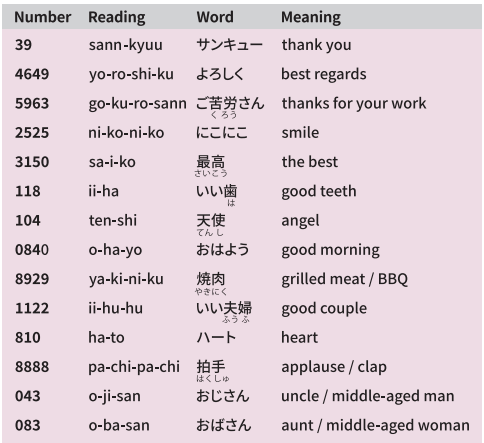
Goro-Awase, Hidden Codes, and Wordplay in Japanese Numbers
数字が語る日本語の世界Japanese numbers carry more than numerical value—they echo sounds, meanings, and even hidden messages. From playful goro-awase puns to coded expressions used online, numbers in Japanese culture often “speak” in creative and surprising ways. Once you begin to recognize these patterns, simple digits start to reveal humor, and personality.
日本語の数字は、単なる数ではなく、音や意味、リズムをもって“語る”存在です。語呂合わせや隠語、ネット表現など、数字は日本語文化の中で多様な役割を担っています。仕組みを知ると、数字の裏に潜むユーモアや感性が見えてきます。
Standard & Useful Goro-awase
一般の語呂合わせ
Hidden slang, BAN-avoidance, and other coded number expressions
隠語・BAN回避などの数字表現On platforms where certain words (death, violence, illness, etc.) may be restricted, Japanese speakers often use numbers to express those concepts indirectly. Some of these codes also come from long-standing slang or subcultural usage.
SNSや動画サイトでは、死亡・暴力・病名などがNGワードになることがあり、数字で言い換える文化があります。また、古くから使われる隠語の数字も存在します。

This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
Controversy Over Cabinet Official’s Nuclear Remarks
首相官邸幹部の「核保有発言」をめぐる論争- Hiragana Times
- Jan 22, 2026
[Pros and Cons with Insights / 賛否と洞察 – February 2026 Issue]
Controversy Over Cabinet Official’s Nuclear Remarks
首相官邸幹部の「核保有発言」をめぐる論争
Background | 背景
At the end of 2025, a Cabinet official stated that “Japan should also possess nuclear weapons,” triggering widespread controversy.
2025年末、首相官邸幹部が「日本も核を持つべきだ」と発言し、波紋を広げた。Debate over Japan’s “Three Non-Nuclear Principles” is resurfacing.
日本の「非核三原則」をめぐる議論が再燃している。Pros | 賛成意見
As neighboring nuclear-armed countries strengthen their military presence, Japan should also possess nuclear weapons as a deterrent.
周辺の核保有国が軍事的存在感を強める中、日本も抑止力として核を持つべきだ。Cons | 反対意見
Japan, the only country to have suffered atomic bombings, has persuasive power precisely because it does not possess nuclear weapons. It should continue to uphold this stance.
唯一の被爆国・日本は、核を持たないからこそ説得力がある。その立場を守り続けるべきだ。Insight | 洞察
Nuclear weapons have long been described as “the ultimate deterrent.” But what about the reality?
核兵器は「究極の抑止力」と語られてきた。 だが現実はどうか。Israel, which possesses nuclear weapons, has come under missile attacks, while nuclear power Russia continues a war with no end in sight.
核を持つイスラエルはミサイル攻撃を受け、核大国ロシアは終わりの見えない戦争を続けている。Nuclear weapons may prevent full-scale war, but they have no power to prevent attacks themselves.
核は全面戦争を防ぐかもしれないが、攻撃そのものを防ぐ力はない。“Nuclear weapons ensure safety” is nothing more than a myth.
「核があれば安全」は神話にすぎない。The idea of believing in nuclear weapons as “ultimate power” is a form of monotheistic thinking.
核兵器を”究極の力”と信じる発想は、ある種の一神教的思考である。The idea of forcing others into submission through absolute power itself has generated conflict.
唯一絶対の力で相手を屈服させる――その発想自体が、争いを生み出してきた。In fact, many of the wars that continue today are rooted in clashes of monotheistic “justice.”
現に、今も続く戦争の多くは、一神教的な「正義」の衝突に根ざしている。The Japanese spiritual outlook, in which countless gods coexist, is different from such ways of thinking.
八百万の神々が共存する日本の精神は、そうした思考とは異なる。Is there no way to defend a nation without nuclear weapons?
Japan has a tradition of “softness overcoming strength.”
核を持たずに国を守る道はないのか。 日本には「柔よく剛を制す」の伝統がある。This country should have the potential to create technologies and philosophies that neutralize an opponent’s power.
力を無力化する技術や思想を生み出す可能性を、この国は持っているはずだ。
A time will come when countries that have believed in nuclear weapons as the one absolute god realize that it was a demon.
核を唯一絶対の神と信じてきた国々が、それが悪魔だったと気づく時代が来る。At that time, it will be proven that the country that did not possess nuclear weapons was the wisest.
そのとき、核を持たなかった国こそが最も賢明だったことが証明される。
This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
A Television Culture That Has Shaped Japanese Mornings
日本人の朝をつくってきたテレビ文化- Hiragana Times
- Jan 22, 2026
[Close up Japan – February 2026 Issue]
A Television Culture That Has Shaped Japanese Mornings
日本人の朝をつくってきたテレビ文化
In Japan, NHK’s morning serial drama, commonly known as “Asadora,” airs at 8 o’clock in the morning on weekdays.
日本では平日の朝8時、NHKの朝の連続テレビ小説、通称「朝ドラ」が流れます。
This Asadora, which began in 1961, has accompanied the daily lives of Japanese people through 15-minute episodes.
1961年に始まったこの朝ドラは、1話15分の物語で、日本人の日常に寄り添ってきました。
Rather than flashy developments, the careful portrayal of family, work, and the passage of time is its defining feature.
派手な展開よりも、家族や仕事、時代の移ろいを丁寧に描く点が特徴です。
“Oshin,” which aired in 1983, depicted a woman who endured poverty and survived, and received high acclaim overseas, including in the Middle East.
1983年放送の『おしん』は、貧しさに耐え生き抜く女性を描き、中東を含む海外でも高い評価を受けました。

Asadora, while being Japanese stories, has conveyed universal human emotions.
朝ドラは、日本の物語でありながら、普遍的な人間の感情を伝えてきました。
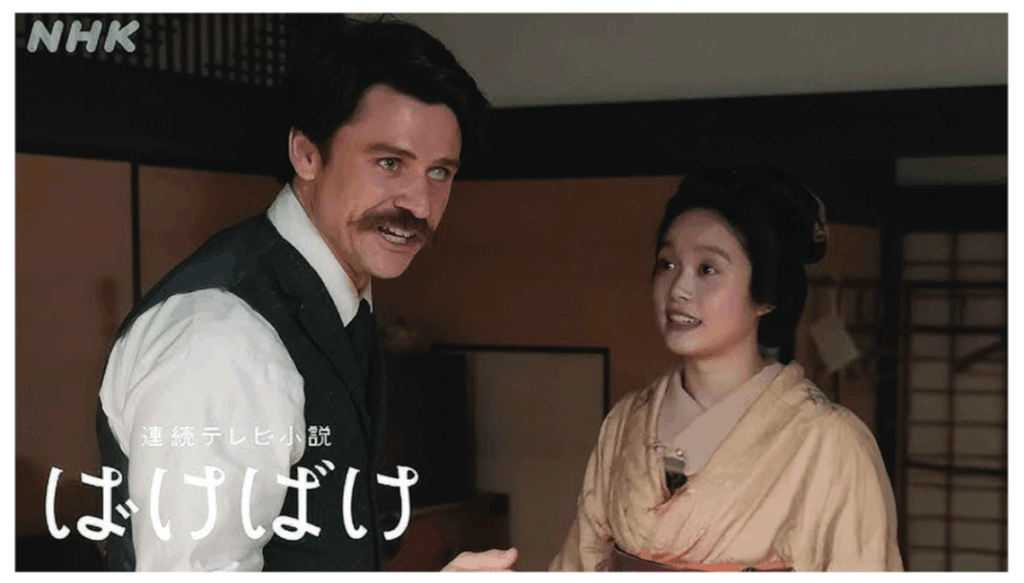
What that Asadora is currently depicting is “Bakebake.”
その朝ドラが現在描いているのが、『ばけばけ』です。
The model for the protagonist is the writer Koizumi Yakumo, who was active during the Meiji period (1850–1904).
主人公のモデルは、明治期(1868年〜1912年)に活躍した作家・小泉八雲。
He is a Greek-born Westerner of Irish descent, known in the West as Lafcadio Hearn.
彼は西洋ではラフカディオ・ハーンとして知られる、ギリシャ生まれのアイルランド系西洋人です。

After working as a journalist in America, he came to Japan out of an interest in Japanese culture, and eventually became a naturalized citizen.
アメリカで記者として活動したのち、日本文化への関心から来日し、やがて帰化しました。
He was fascinated by the spiritual culture of the Japanese people, such as ghost stories, yokai, and folk beliefs, and introduced them to the world in English.
怪談や妖怪、民間信仰といった日本人の精神文化に魅了され、それらを英語で世界に紹介しました。
In them is embedded a uniquely Japanese sensibility—not only fear, but also reverence for nature and coexistence with the dead.
そこには、恐怖とともに、自然への畏れや死者との共存という日本独自の感性が込められています。
The title Bakebake comes from the word bakeru (“to transform”) and symbolizes a worldview in which invisible things reveal themselves.
タイトルの『ばけばけ』は、「化ける」という言葉から来ており、見えないものが姿を現す世界観を象徴しています。
This quiet 15-minute morning story continues to reflect the depths of Japanese culture even today.
静かな朝の15分の物語は、今もなお、日本文化の深層を映し続けています。

This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
[New Expressions & Buzzwords – February 2026 Issue]
横転 | Falling-over
😯 横転
pronounced: Outen
definition: Falling-over
It is an internet slang used when someone is surprised.
びっくりした時に使われるネットスラングです。
In Japanese comedy, performers sometimes make falling-over reactions when a situation develops differently from what was expected or anticipated.
日本のお笑いでは、期待や予想と違った展開に、ずっこけるようなリアクションをとることがあります。
“Outen” is used as a word to express such a falling-over–like feeling.
横転は、そうしたずっこけるような気持ちを表す言葉として使われます。
The original “outen” means something like a car falling over on its side.
もともとの「横転」は、車などが横倒しになることを意味します。
This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
[New Expressions & Buzzwords – February 2026 Issue]
チャッピー | ChatGPT
💻 チャッピー
pronounced: Chappi-
definition: ChatGPT
It is a nickname for the generative AI service “ChatGPT.”
生成AIサービス“ChatGPT”の愛称です。
Because “ChatGPT” is a little long, an abbreviated way of calling it has spread among young people.
“ChatGPT”だと少し長いため、若い人の間で省略した呼び方が広がりました。
Recently, the number of people who consult AI about their worries has also been increasing.
最近では、AIに悩みごとを相談する人も増えています。
By calling it by a nickname, a sense of closeness is created as if talking with a friend.
愛称で呼ぶことで、まるで友達と話しているような親近感が生まれます。
This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
[News Review – February 2026 Issue]
The Kanji That Represents the Mood of Society in 2025
2025年の世相を表す漢字
The 2025 “Kanji of the Year” was announced at Kiyomizu Temple in Kyoto.
2025年の「今年の漢字」が、京都の清水寺で発表されました。
The kanji of the year, written on a large sheet of Japanese paper, is “bear.”
大きな和紙に書かれた、今年の漢字は「熊」です。
One reason it was chosen is that bear-related damage occurred repeatedly across the country.
選ばれた理由には、全国で熊による被害が相次いだことがあります。
Another reason is that pandas were returned to China.
また、パンダが中国に返還されたことも、理由の一つです。
The “Kanji of the Year” is decided each year through public submissions.
「今年の漢字」は、毎年、一般からの応募によって決まります。
“Bear” received the highest number of votes, totaling 23,346.
「熊」は、最多となる2万3346票を集めました。
Second place went to “rice,” which became a topic due to rising prices, with a difference of only 180 votes.
2位は、価格高騰で話題になった「米」で、その差はわずか180票でした。
The “Kanji of the Year” began in 1995. This is the first time that “bear” has been selected.
1995年に始まった「今年の漢字」。 「熊」が選ばれたのは、今回が初めてです。
This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
-
[Cover story – February 2026 Issue]
The Grand Sumo Tournament — Dohyō-iri
大相撲初場所 ―― 土俵入り
On Sunday, January 11, Reiwa 8 (2026), the Grand Sumo Tournament will be held at the Ryōgoku Kokugikan in Tokyo.
令和8年1月11日(日)、大相撲初場所が東京・両国国技館で開催されます。
To mark the beginning of the new year, this issue’s cover features “Inuta Kobungo — The Grand Sumo Tournament,” a work by Gakyōjin Bunta Inoue.
新年の幕開けに合わせ、今月号の表紙は、画狂人・井上文太氏による作品「犬田小文吾・大相撲初場所」です。
What is depicted is a scene from the ring-entering ceremony of professional sumo.
描かれているのは、大相撲の土俵入りの場面です。
The rikishi (wrestlers) are lined up in a circular formation, and at the center stands Inuta Kobungo, a character from Nansō Satomi Hakkenden, serving as the gyōji.
力士たちが円を描くように並び、その中央には南総里見八犬伝に登場する犬田小文吾が行司として立っています。
On the rikishi’s ceremonial aprons are depicted auspicious motifs suitable for the New Year, such as pine, bamboo, plum, the rising sun, and Mount Fuji, expressing the entire dohyo as a festive space.
力士の化粧まわしには、松・竹・梅や日の出、富士山など、正月にふさわしい縁起物が描かれ、土俵全体が祝祭の空間として表現されています。
Inoue is also known for having designed the ceremonial apron worn by former ōzeki Baruto at the tournament where he achieved his first championship victory, and is an artist who deeply understands the spiritual nature of sumo.
井上氏は、かつて元大関・把瑠都が自身の初優勝を果たした場所で締めた化粧まわしを手がけたことでも知られ、相撲の精神性を深く理解するアーティストです。
From the fact that two pillars are depicted behind the dohyo, it can be seen that this work portrays sumo as it was before the September 1952 tournament.
土俵の後ろに二本の柱が描かれていることから、本作は1952年(昭和27年)9月場所以前の相撲を描いたものと分かります。
The origin of the circular dohyo lies in the ring formed by spectators who naturally gathered to watch sumo, and the suspended roof adopted after the removal of the pillars was a development to preserve a space where the dohyo could be seen from anywhere.
土俵が円形である原点は、相撲を見ようと自然に集まった見物人の人垣が円を成したことにあり、柱を廃したつり屋根も、どこからでも土俵が見える場を守るための発展でした。
The four tassels hanging from the suspended roof represent the deities that protect the seasons and the cardinal directions, indicating that the dohyo is a sacred space.
つり屋根に下がる四つの房は、四季と方位を守る神々を表し、土俵が神域であることを示しています。
Sumo is not a competition, but a Japanese ritual passed down to pacify the earth and to pray for abundant harvests and peace on such sacred ground.
相撲は競技ではなく、こうした神域で大地を鎮め、五穀豊穣と安寧を祈る日本の神事なのです。
This article is from the February 2026 issue of Hiragana Times.
この記事は、月刊誌『ひらがなタイムズ』2026年2月号より掲載しています。
Information From Hiragana Times
-
 February 2026 Issue
January 21, 2026
February 2026 Issue
January 21, 2026 -
 January 2026 Issue – Available as a Back Issue
January 15, 2026
January 2026 Issue – Available as a Back Issue
January 15, 2026 -
 December 2025 Issue —Available as a Back Issue
November 20, 2025
December 2025 Issue —Available as a Back Issue
November 20, 2025